AudioVisual Data in DH
Another Type of Human Narrative: Visualizing Movement Histories Through Motion Capture Data and Virtual Reality
Introduction
Human narratives are one of the most compelling and versatile information sources. One specific category, oral histories, “play a unique role in to documenting cultural heritage and in preserving memories of historical and everyday events” 1. These verbal narratives have traditionally been recorded in audio, video and as written transcriptions. Based on the importance of how an oral history is performed 2 and of how much information physical gestures and facial expressions can convey 3, a question arises about whether the media formats listed above sufficiently capture all the nuances of non-verbal information. By extension, there is also a question of whether all memories can be verbalized and if other means of expression are better suited for communicating the content of those memories.
The issue of performance and non-verbal information within an oral history poses a complex translation problem. Video recordings or “videohistory” helps capture physical movement and nuances that audio recordings and transcripts cannot 4. Furthermore, certain kinds of cultural experiences cannot be fully described using only words. A concrete example of this are descriptions of symbolic poses and gestures used for complicated rituals. Similarly, physical interactions between individuals and their reactions to situations also lose their nuance when described verbally or through controlled cinematography. From an ethical standpoint, voice and photographic images can be potentially compromising even if censored or modified. This may be important if a memory includes some form of physical trauma, distress or injury. Based on the notion that an oral history is the verbal recounting of an experience, then it could be posited that a movement history is a kinesthetic rendering of lived human experiences where identifying voice and visuals could be obscured if needed.
With these factors in mind, I propose that the concept of a “movement history” be considered for memories that are based in physical embodied experiences which can be difficult to describe with only words or depict using photographs and video. This definition reflects Albert Lichtblau’s statement that “physically active remembering also influences the narration, especially when psychology and mentality can be brought into contact with the past 5. Additionally, I recommend that movement histories be captured and presented in a way which enables a viewer to see all angles and details of the movement rather than be restricted to a single angle or framing. It is currently easiest to achieve this effect by combining mocap and VR technology with the understanding that other technologies may be used in the future.
I begin my exploration of this concept by reviewing how the evolution of oral history practices can lead to the creation of movement histories. For this article, I will focus on illness narratives expressed through somatic movement practices with my own movement history, Lithium Hindsight 360 as a case study. Following that I offer some practical insights from my own experience as a motion capture (mocap) and virtual reality (VR) researcher to offer practical tips and relatively affordable technology solutions. One key issue will be the dissemination and accessibility of the mocap data as there is still a usability barrier in the form of technological devices. Additional resources tailored to content creators helping to maintain the movement dataset and accompanying visualization interfaces are also suggested.
Background
The roots of this article started in my previous research on digital dance preservation. As a choreographer and digital archivist, I was intent on finding a practical way to preserve human movement as accurately as possible. At first I believed very strongly in all the existing preservation practices, whether it was collecting good metadata, using high quality video for documentation or ensuring that a repository followed the Open Archival Information System [OAIS] model. These practices worked well in the archives and libraries where I worked, but were not so feasible as an independent artist working alone. From an archivist’s perspective it meant processing haphazardly maintained content. From a choreographer’s perspective, it was frustrating to be unable to see and analyze all the nuances of how a dance work was performed.
In 2013, I started to become more invested in the Boston dance community and its history since the 1950s. In an effort to fill gaps in the existing documentation, I was inspired by The Dance Oral History Project created by the New York Public Library 6.
“Bebe Miller Interview, Excerpt.” Source credit: New York Public Library. https://www.nypl.org/audiovideo/bebe-miller-interview-excerpt.
By luck, dance scholar Jeffrey Friedman happened to be teaching an oral history workshop in Boston around this time. Hearing him talk about dance-specific examples was very useful as I prepared to conduct my own interviews. Very quickly, however, I encountered the same problem that had plagued me for documenting dance: how does one verbally describe movements that defy words?
This problem eventually formed the basis for my practice-based research on creating movement-based pathographies. My original motivation for using mocap and VR was to give patients and viewers alike a sense of privacy. After constructing my initial prototype, however, I realized another benefit. By using mocap data to create an animation viewable in VR, viewers could have complete freedom to examine the movement from any angle or distance. In some ways this meant a more unbiased form of moving image documentation in that the framing of the content had not been decided for the viewer.
I also began to notice some similarities between illness narratives and pathographies with oral history which I address later in this article. The most obvious commonality is the autobiographical narrative based on an individual’s memory. This common trait thus made me start to wonder about the possibility of movement-based equivalent to oral history – that is, a movement history.
Oral History into Movement History: Mutable Memories
Oral history was originally considered the domain of historians and has since been adopted by a variety of disciplines such as ethnology, anthropology and sociology as well as used for social work and community-led projects 2. For example, a local historical society may conduct oral histories to help a community learn about its past 7. Guidelines and instruction courses for how to conduct an oral history are available but there is technically no single correct way to engage in oral history 3. In terms of specific activities, Lynn Abrams describes oral history as consisting of three main components: 1) an interview process and product of interview, 2) research methodology and result of research process and 3) an act of recording and final record 2.
At the core of any oral history is a human memory. These memories usually reflect recollection of and/or commentary on significant events, although they may also be centered on daily life or more private events. The fact that these memories are not always precise 8 can be seen as problematic or beneficial in that it can affect the accuracy and presentation of content. To avoid frustration, interviewers are encouraged to think of oral history as a shared responsibility with those whom they are interviewing 3. To that end, the extent to which an oral historian must gain the trust of their subjects is no small matter. When this trust is well-placed, a potential platform for communicating information through narratives is created. This platform can be useful for bringing awareness to marginalized communities and hidden histories 2.
Although visual content may help supplement verbal descriptions, the perspectives are often limited or curated by the documenter. Sometimes a lack of aural clarity or a need to adhere to “filmic language” can also interfere with accurately capturing all the information provided 4. Given the rapid developments in 21st century audio/video technology, it is increasingly easier to supplement oral histories with additional information or options for interaction. An example of this would be the University of Southern California Shoah Foundation’s Dimensions in Testimony exhibition which combines holographic projections, voice recognition and natural-language processing 9. This immersive way of viewing and interacting with a subject speaking their oral history could generate a deeper understanding as it would allow users to change distance, angle and relationship to the subject. At the same time, the use of multimedia technology must make logical sense given the costs, logistics and ethics involved 10.
To address the issues of providing an enhanced viewing experience without being extravagant in one’s technology choices, it may be useful to look to the field of dance for performance strategies that can help add nuance. The connection between dance and oral histories is that dances are a part of oral tradition that can be intangible and ephemeral in such a way that challenges the act of documentation itself 11. Furthermore, “Dance also challenges other experts to think about devising imaginative methods or scoring, notating, annotating, and archiving a processual, somatic, and multisensory practice” 11. Since a movement history is still based on a personal memory, it would be logical to look at how somatic dance forms that embrace the unique attributes of an individual body for strategies on how to recall, express and perform embodied experiences in a physical manner.
Somatic movement practices often require practitioners to explore the idiosyncrasies of their bodies and their relationship to other bodies in a way that generates a sort of autobiography. These movement practices can also be used to literally illustrate life events which leads to a form of double-layered autobiography. Improvisational methods may incorporate internal and/or external questioning which then becomes reminiscent of an oral history interview. The range of somatic movement practices range from the Asian disciplines of yoga and tai chi to more recent systems such as Feldenkrais and Body Mind Centering. Within that spectrum lie somatic dance forms that have become increasingly used for artistic expression: Authentic Movement, Contact Improvisation and Skinner Releasing Technique amongst others. Steve Paxton, founder of Contact Improvisation, was known for his Small Dance ritual which guides the individual to examine their own body. This self-examination was later part of Paxton’s documentation about his process which essentially served a sort of autobiography of his body 12.
Similarly, Bill T. Jones, who also used Contact Improvisation, created several solos based on both his own life events and his body’s mechanics. Jones helped pioneer the combining of somatic movement practices with motion capture technology. The particular nature of Jones’ works yielded what could be considered a type of movement history. An early example would be the 1999 Bill T. Jones collaboration with the Open Ended Group, Ghostcatching . Originally intended to challenge the boundaries of the human body 13, Ghostcatching was not intentionally autobiographical but in the end took on autobiographical elements specific to Jones 13.
Similarly, the motion capture samples performed by Steve Paxton as part of his research on contact improvisation that started in 1986 and were released on DVD-ROM in 2008 were not necessarily autobiographical 12.
More recently, somatic movement experts such as Ruth Gibson are more consciously adapting their technique to the limitations of mocap systems 14 and taking a phenomenological approach to mocap recording for VR environments 15.
An Overview of Motion Capture, VR and Somatic Movement Practices
The integration of new technologies into oral history practice is not unusual. Digital technology in particular can be integrated across all aspects of the process, whether it is in recording, archiving or disseminating content 16. It is therefore reasonable to assume that oral history can evolve to the next level of incorporating virtuality. This is already present in projects such as the previously mentioned Dimensions in Testimony exhibition. Virtuality can be used for various purposes whether it is to increase access, create a sense of immersion, generate a sense of embodiment or any other number of reasons. For movement histories, the goal is to allow viewers to examine physical memories without being invasive to the source. To that end, mocap and VR can help create a safer way to view and interact with such content.
Mocap data is extremely versatile in that it can be used for everything from scientific motion analysis to mainstream entertainment. Conceptually mocap has its roots in Eadweard Muybridge’s animation experiments and Max Fleischer’s rotoscope device 17. Technologically, the systems used at the time of writing descend from motion tracking systems developed in the 1970s and 1980s. One such example are the point light displays developed by Gunnar Johansson 18. Since then a variety of systems have been released such as sensor-based systems that rely on accelerometers and camera-based optical systems using infrared markers. The latter type of system allows for reliable tracking and orientation of joints 18 and accurate capture that enables a variety of data interpretation and facings 19.
The visualization of this mocap data can also help with human movement analysis 11. Although mocap data can be visualized in both 2D and 3D spaces, the latter option allows viewers full rein over perspective within a 6DOF (degrees of freedom) interactive context. The term “6DOF” refers to the three directions in which the head can move (3DOF) combined with the three directions in which the body can move through space 20 An added benefit of VR is that it is fully immersive and therefore visual distractions can be eliminated. Untethered headsets such as the Oculus Quest provide additional freedom in movement. This adds to a sense of immersion which can be a useful element for supporting a narrative. Previous concerns about motion sickness and ergonomic issues 21 are being addressed through improved headset design, increased graphics computing power and a generally better understanding of VR design principles. Researchers such as Michael Madary and Thomas K. Metzinger have released recommendations for more ethical design 22 and constant updates in software platforms and standards also contribute to an improved experience. Another benefit of using an immersive environment is the ability with which it is possible to blend both visual and aural media with sound playing as vital a role to immersion as visuals. This balance between types of media may help address Mark Tebeau’s concerns about overemphasizing visual representations of oral histories and the need for novel ways of data visualization 1.
Illness Narratives in Oral History and Somatic Movement Practices
The concept of phenomenology or “the experience of” is very relevant to memories. A specific type of memory rooted in phenomenology is the illness narrative. The purpose of an illness narrative is to share a patient’s perspective on experiencing symptoms, treatment, stigma and other aspects of an illness 23. This perspective may agree or contrast with a medical professional’s. Like oral histories, illness narratives can focus on specific incidents, lifelong stories or become part of a collection of multiple narratives. More importantly, certain types of patients such as the chronically ill can be categorized as part of a marginalized and/or silenced group who are able to regain their voice through sharing their stories 24. Abrams states that “Oral history was intended to give a voice to the voiceless, a narrative to the story-less and power to the marginalized” 2. From this perspective, the collective experiences of patients can potentially reflect hidden truths about society.
Within the history of medicine, the use of oral history has evolved significantly over time. Oral histories were initially conducted for male figures of influence in medicine before taking on a social history role in the 1970s and a supporting evidence role in the 1990s 25. It was the course of this evolution that the question of how to provide a patient’s history as opposed to that of a doctor’s came into existence. Scholars such as Arthur W. Frank and Arthur Kleinman would start to collect and analyze the narratives of patients while G.Thomas Couser would start to bring the term “pathography” forward into the 20th century.
Some debate would be spurred by Anne Hawkins’ very specific definition of pathography in that it is limited to a written account of physical illness 24. Her approach would later be challenged by performing arts scholars such as Alex Mermikides and Gianna Bouchard who identified theatrical performance as a type of “embodied pathography” 26.
Kay Jamison’s autobiography as a patient with bipolar disorder 27 and Kerry Davies’ collection of mental patient narratives would also challenge the focus on physical illness 28. Most importantly, the recognition of the invisibility of patients 25 and how narratives can help with self-awareness and regaining personal agency 28 elevates the importance of enabling patients to communicate their stories.
Several traditional oral history collections currently exist, including several on mental health. They include the oral histories of disability and personal and mental health collections at the British Library 29, the Australian Generations Oral History Project 30 and the Schizophrenia Oral History Project 31. There also exist dance and other movement-based works which are based on a patient experiences. As an art form, illness narratives have been created and shared by professional dancers for centuries with classic examples being the madness scene in Giselle and a deathbed duet in Manon .
As a non-dramatized account performed by a patient, however, illness narratives become subject to moral and ethical complications. In some cases, an illness is accompanied by feelings of helplessness, shame and/or stigma as expressed by Havi Carel in her account of struggling with lymphangioleiomyomatosis 32.
For attendees of Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance patient support meetings, the confidentiality requirement is a reminder that sharing identifying information about a patient may have negative consequences 33. The outcome is reminiscent of other marginalized or endangered communities where survival is dependent on obscuring identity. In a positive light, sharing an illness narrative can lead to greater understanding and advocacy for improvements in social infrastructure for patients.
One of the pioneers in this area would be Anna Halprin. Although her solo works such as Portrait 34 were more intended to heal her own cancer rather than simply depict the experience of cancer, she would later proceed to create works about the experiences of others. One such work, Intensive Care: Reflections on Death and Dying 35, is based on her husband’s hospitalization. Similarly, Bill T. Jones’ 1994 Still/Here is based on the stories of actual patients with life-threatening conditions 36.

“Still/Here.” Please see video here. Source credit: Numeridanse.
The contrast between Intensive Care and Still/Here lies in the ethical complications surrounding both pieces. In Halprin’s case, she performs in a piece about someone with whom she had a close relationship with. Still/Here , on the other hand, is Jones’ interpretation of stories that he collected from others before presenting it on the bodies of professional dancers. This question of whether such a deeply personal story should be depicted by an outsider calls to mind Susan Kozel’s challenging of Daniel Dennett’s notion of the heterophenomenologist 37. While heterophenomenology is not inherently unethical, the value of such a practice becomes more questionable when the experiences of traditionally silenced and/or vulnerable populations are being presented through the lens of an external neutral observer.
Case study: Movement-based Pathography
The concept of phenomenology is the central driver for illness narratives as evidenced by the research of aforementioned medical humanists Frank and Carel as well as S. Kay Toombs and others. Within narrative medicine, phenomenology refers to the experience of having an illness, whether referring to the sensation of symptoms, daily living and/or contextual experiences 32. It therefore makes sense to extend the narrative medicine approach to movement-based illness narratives regardless of documentation method. For my own work Lithium Hindsight 360, a set of somatic movement-based illness narratives about bipolar disorder, I referenced the VR ballet [pain]Byte developed by Genevieve Smith-Nunes 38. Both Lithium Hindsight 360 and [pain]Byte are based on the lived experiences of their respective creators with an emphasis on community engagement. Anonymizing the identities of the mocap performers for ethical purposes was another common factor.
In order to generate the movement histories presented in Lithium Hindsight 360 , I combined several somatic movement practices to translate the experience, structure the movement and perform the memory. I chose this approach because I noticed that universally relatable physical gestures and movements being expressed by mental health patients while sharing their experiences in a group setting. Examples might include hand tremors, moving slowly due to exhaustion or agitated rapid gesticulation with the arms. For translating and structuring memories into movement, I adapted the Life Art Process to help me identify key positions and gestures with specific experiences. To do this, I first compiled a list of commonly known adolescent bipolar disorder symptoms, read the individual testimonials in medical reports and then tried to translate what I had read. Based on that experience, I decided that it was more appropriate to use my own bodily experience as a patient with bipolar disorder. This decision lead to the creation of two different scenes, “Symptoms” and “Maintenance”.
In “Symptoms”, individual symptoms are depicted by a group of mannequins that resemble each other. They are anchored by a mannequin attempting to ask for help but unable to articulate its needs. Presenting the physical movements without an explanation of the symptom can make a viewer pause and rethink their previous understanding of what a mental health condition looks or feels like. For “Maintenance” viewers are taken through a standard day of waking up, taking medicine, anxiety over interacting with others, exhaustion from feigning good health and then the return to bed. This scene has a more traditional dance sequence as I used to dance to relieve anxiety and stress. The majority of the movement is more pedestrian to the point of almost looking like pantomime. Since the predominant physical feeling was the sensation of constantly falling apart, the avatar is also constantly shifting and appearing to disintegrate before stabilizing again.
To perform and generate all of the movement, I used various forms of improvisation methods including Contact Improvisation and Authentic Movement to sequence the positions and gestures into a narrative. At this level, I was not thinking about using specific vocabulary from a technique. Instead I was adapting concepts such as initiating movement from an internal point or using a video camera as my “witness” rather than a person. Taking this approach helped me avoid “performing” or overdramatizing my movements. Finally, my own movement style or “voice” is influenced by martial arts forms such as tai chi. This results in movement that is alternatively fluid and percussive.
Initially I had thought it would be better to translate the experiences of other patients with bipolar disorder as presented in medical reports similar to what Jones had done with his choreography. When I realized that this type of heterophenomenology exacerbates issues raised by Susan Kozel about agency and representation that could lead to silencing 37, I made the decision to use my own movement history of being a patient. If this type of heterophenomenology is done in conjunction with patients then it may be ethically possible and accurate for a third party to portray the experiences of another even without a close personal relationship.
Practical Strategies and Considerations
Two of the first assumptions that might come to mind when beginning a mocap and VR project is that it is very expensive or technically difficult to generate. In the earlier days of mocap and VR this would have been accurate given the experimental nature and limited access to technologies. As of 2020, there is a constantly growing range of consumer-level hardware and software tools that are still capable of producing high quality results. The simplification of user interfaces and procedures enables creators and researchers to think more holistically about their approach rather than having to become expert programmers and technicians. In this section I offer tips generated from discussions with some of the experts referenced in this article as well as my own personal experiences with multiple hardware systems and recording scenarios. For further details on tasks such as selecting a mocap system, data clean-up, preservation and getting started with a project, please see the Appendix.
In terms of performance, the most important factor is to remember that there is a difference between documenting, performing and performing for documentation purposes. Subjects may need to exaggerate their movements slightly to avoid occlusion issues. This too depends on the type of system and the level of subtlety being captured. For example, a motion sensor like the Kinect can capture full-body, facial and finger data with a single device.
Using a marker-based system, however, allows for more detail refinement later in the visualization stage. Extra set-up time and warm up takes are also recommended as it allows the subject to become accustomed to the direct or indirect impact of a mocap system on their body. This is similar to the process of an interviewer engaging with their subject before conducting an oral history interview.
Other useful strategies can be found in the work of dance movement researchers. In her overview of mocap dance, Kim Vincs reminds readers that concepts such as gravity, race, and gender can all be manipulated in post-production 39. This manipulation eases the pressure for a “perfect” performance and provides the option of hiding certain physical traits. More technical factors such as pre-acceleration of the body and thinking in terms of motion trails rather than shapes may help with recording cleaner data. Movement artist-researcher Steph Hutchison conscientiously adapted her practice to the requirements of a mocap system to yield better results 40. One practical modification was in thinking of the markers on her body as “partners” to work with rather than struggle with.
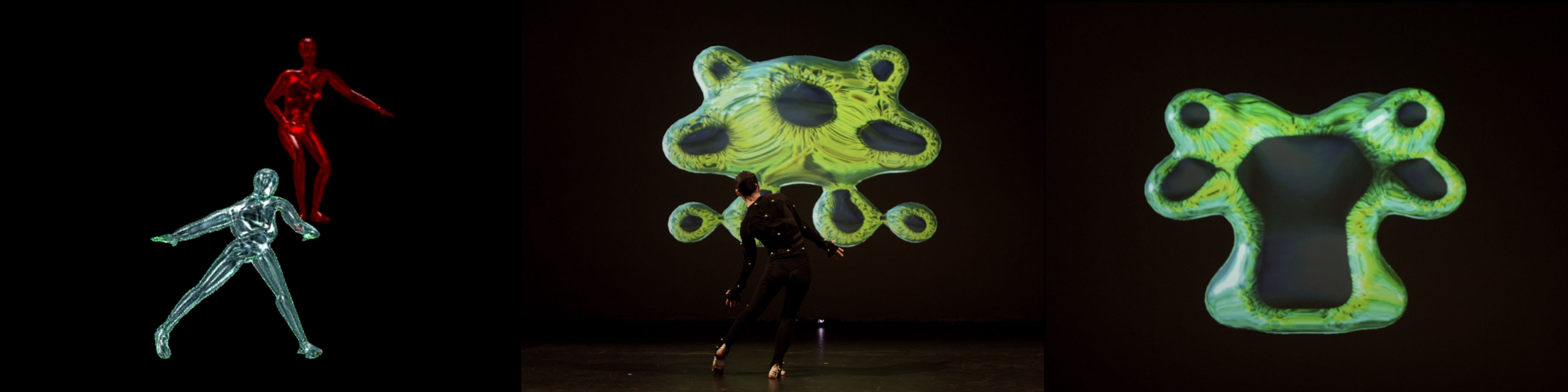

“Recognition Steph Agent Avatars Blobs Tryptic Emergence.” Source credit: Steph Hutchison.
At the time of writing, it is generally recommended to conduct shorter takes of a movement history for several technical reasons. The first is that a system can glitch out which would then affect the system calibration and therefore render the rest of the mocap data unusable. This glitching can happen regardless of whether an inertial, optical or other system is used. Another reason is that most human bodies have a limit for how long they can continuously move. A trained body may be able to move continuously for a long time whereas a less active person may be fatigued after several minutes. Finally a long take will lead to a larger file that may be harder for an animation software to process and visualize. The mocap recording process will usually yield several files per session, so a consistent file naming scheme and stable storage system is essential. This may seem like a routine course of action but these steps can easily be forgotten when caught up in the moment or pressed for time. Finally, if a transcription and analysis of the movement is necessary, it may be useful to use systems such as Labanotation and Laban Movement Analysis. Both Labanotation and Laban Movement Analysis (LMA) were based on the work of modern dance pioneer Rudolf Laban 41. Labanotation is a graphical method of notating movement while LMA is a method for describing the quality and motivation of movement. The two systems can be used together or separately.
When recording, it is important to avoid simply documenting the memories through recording them and to remember that access, storage and preservation are part of this process as well 42. Although this fact may seem normal to any archivist, librarian or other information professional, it is not always obvious to laypersons. A significant difference between movement histories and artistic works using mocap is that a history focuses on authentically presenting what has been practiced or lived whereas artistic works typically strive to create a certain aesthetic or explore the differences between each performance of said work. Therefore the need to preserve multiple iterations of a history or striving for a technically perfect performance is eliminated.
On a technical level, there are some challenges specific to the preservation of mocap data and VR projects. In 2006 it was already noted that the quantity of mocap data produced from a session could be quite large and was not easily searchable 43. WhoLoDancE repository tools have optimized searchability of movement to a certain degree 44 but a mainstream non-textual search engine has still yet to emerge in any discipline.
From a VR perspective, one must decide whether to use an existing game engine such as Unity or engineer a bespoke solution. Further objects such as 3D models, texture maps, supplementary audio and video may also need to be taken into consideration. Fundamentally, the digital curation of movement histories comprised of mocap data and VR projects is the same as for any other set of digital objects in that standardized file formats (i.e. fbx, bvh) used across multiple industries are typically used for the source objects. If anything, the most challenges lie in the lack of a standard file format for gaming engines such as Unity and Unreal. Constant changes in both hardware and software also make it difficult to pinpoint a single ideal long-term (>25 years) file format for any of the objects contained within a VR project.
Given the rapid evolution of mocap and related technologies, the practical solution would be to focus on maintaining and migrating mocap data with the expectation that the visualization of that data will change over time. This is not to belittle the work that goes into creating VR environments. Instead, by focusing on movement as the primary source of information, the content can be made more accessible since it could be visualized in multiple ways. In an ideal setting, digital preservation practices such as using repositories built on the OAIS (Open Archival Information System) reference model and metadata standards would be expected. Implementing such practices, however, also comes with a significant cost 8. To help relieve the burden on data stewards, it may be useful for movement history creators to reference the strategies of existing artists’ toolkits 45 and habits of new media artists 46. Furthermore, the previously theoretical concept of networked digital archives 47 has already materialized in the form of widespread cloud computing services. The need for large and flexible storage space is better served by these services than traditional servers.
Conclusion and Future Evolutions
In the past, the recording of mocap and its subsequent visualization was technically complicated and costly. The process of mocap is still not as simple as making an audio recording, but evolutions in digital technology certainly make it easier. Similar things could be said about VR as new tutorials, hardware sets and software solutions continue to be released. For the immediate future, the most frequent use of movement histories might be as a complementary pairing with oral histories. Examples include a voiceover accompanying an illness narrative using mocap or a written account of a traumatic event accompanied by movement illustrating key moments. A future concern for this type of visualization is that of enabling accessibility for the visually impaired 10. In the future, haptics might be able to help resolve vision impairment or reliance on text by conveying a different type of a sensory information. The initial work conducted at Deakin Motion Lab and the Institute for Intelligent Systems Research and Innovation (IISRI) that integrates social haptics with dance to create an embodied experience through kinesthesia 19 may well lead to being able to completely experiencing the physical memory of another individual.
On a more personal level, I had two major revelations while constructing my own movement history. The first discovery was that the reactions to my LH360 experience often reflected more about a viewer’s previous perceptions about mental health and the communities they came from than any truth or understanding about the experience being shown to them. In other words, it was possible to induce reflexivity and intersubjectivity through presenting abstracted movement in an immersive environment. Patients would express relief and motivation that someone else was sharing an experience similar to theirs. Non-patients would question their previous perceptions of mental health patients. As I had never encountered this kind of reaction when similar movement was presented as a live performance, I was extremely surprised by this result. Presenting the VR experience and the publications about it have also brought me into contact with a wide range of artists and researchers working on similar projects.
These kinds of connections and discoveries are why I became an interdisciplinary practice-based researcher in the arts rather than an artist, archivist or other type of humanities researcher. Traditionally, artistic practice is supposed to speak for itself through the artistic work itself and academic research should be presentable through textual publications. Yet there are still forms of human-generated content that are too multi-faceted to be presented using only one kind of media or without contextual information. The LH360 development process relied on methodologies such as autoethnography, reflective practice and user experience design as well as an understanding of various artistic technique. Furthermore, I received comments that viewing the VR experience enhanced an understanding of its associated publications and vice versa. Based on my experience with creating LH360 , I believe that forms of artistic expression can be utilized for purposes other than creating pure works of art or entertainment. The concept of an artistic practice-based researcher has been acknowledged in academic circles since the 1980s 48 49 which means that there are pioneers to look up to, a current peer community, and most likely an increase in this type of researcher. Regardless of whether one comes from an academic, artistic or hybrid approach, increasing developments in visual, aural, and haptic technologies should make it more feasible to reproduce non-verbal content that addresses all the senses. Over time, these innovations may lead to more multi-dimensional presentations of individual memories, historical events and entire cultures.
Appendix: Choosing Hardware and Software Options
The first thing that researchers should consider is their choice of mocap system. Ideally the system should be chosen based on the type of movement recorded, frequently used body part(s), portability and need for anonymity. It may be tempting to choose a system for its cost, convenience or availability but this can later create problems. A comparison of several systems is provided below to illustrate how the attributes of a system could be problematic or simply not useful for a researcher. The information is a combination of general knowledge and my personal experience using the listed system. It is by no means an extensive listing of all systems currently available on the market. For a more detailed look into mocap systems, I recommend reading the white paper released by Epic Games in May 2020.
System Type/Description Unique Attributes Benefits Limitations Microsoft Kinect Depth camera/Motion sensor device Originally a gaming device Excellent for point cloud effects. Very cheap to buy and easy to setup. May need multiple devices. Combining multiple data sources may require a custom software solution. HTC Vive Tracker Inertial/Repurposed trackers Repurposes part of the HTC Vive virtual reality headset package Very portable set-up. Can be used with third party software. The weight of the sensors affected ease of movement Notch Pioneer Inertial/Motion sensors strapped to body Individual sensors are attached to adjustable straps Easy to put on and customize location of sensors. Reasonably priced and expandable. Need smartphone or tablet for recording Perception Neuron Inertial/Wearable sensors in a suit Sensors are attached to a “suit” of straps. Fairly easy to put on and lightweight. Includes a comprehensive software platform. May require frequent calibration. Weight of the battery pack can affect movement. Requires wireless router setup. Rokoko Smartsuit Inertial/Wearable sensors in a suit Can be used almost anywhere. Suit is comfortable and well-constructed. Price is about the same as a high-end laptop. Can be combined with face and hand mocap devices. Separate suits need to be purchased for each person/size. Same battery pack and wireless router issue as Neuron. Cannot accurately measure changes in levels. Optitrack Prime Optical/Passive markers (reflective) Comes in multiple configuration options. Very good software and easy calibration. Can do almost any kind of motion with ease. Easy to use data clean-up tool. The most expensive option. Requires a lot of resources (i.e. computing, electricity, space). Good technician with knowledge of marker setups, calibration, etc. is essential.
Another aspect to consider about choosing a hardware system is the software platform that accompanies it as well as the external software platforms that the hardware can interface with. Software can affect how cleanly motion is captured, provide easier ways to clean up and manipulate the data, or even enable faster sharing. In some situations, the hardware may not be the most robust, but the software makes the rest of the process easier. Most systems will come with their own proprietary software or require use of a licensed program. Ultimately the final decision should take into consideration whether one is recording full body large movements or smaller subtle movements, whether identity is an issue, if factual accuracy is required or if emotional expressiveness is the main priority.
Just like with any other data set, mocap data clean-up is extremely time consuming. The clean-up process usually consists of manipulating coordinates using either a linear graph editor or actual points in 3D space. While there are tools to help automate the process it is useful for researchers to review the raw capture and the cleaned-up version to ensure that vital details are not accidentally erased. By contrast, mapping the data to a 3D model to generate an animation can be relatively quick so long as the skeleton has been properly mapped.
Based on existing practices from commercial industry as balanced by financial limitations, I would recommend the following hardware, software, digital object and project planning starting points for researchers engaging in mocap and VR for the first time. Factors include cost of renting or purchasing a mocap system, personnel time and compensation and whether the project is being worked on a full or part-time basis.
Ideal Expensive Setup Moderate Investment Setup Basic Setup
Marker-based/optical system with knowledgeable technician (Optitrack is good) Programmer with knowledge of Unity or other visualization software 3D modeler for custom figure and environment At least 2 sessions at 2 hours each for a short recording 3 months of dedicated time for visualization
Portable sensor suit system Unity or software template A way to customize a stock 3D figure and environment At least 2 hours for the recording session 3 months of partial time for visualization
Notch, Vive or Kinect type system WebVR template using frameworks such as A-frame Stock 3D figure for free and mapped photos Keep interview very short and shoot as best as possible No deadline for completion of visualization
. Tebeau, M. “Listening to the city: Oral history and place in the digital era” Oral History Review , 40.1 (2013): 25-35. ↩︎ ↩︎
Abrams, L., Oral History Theory . Milton Park and New York (2010). ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
Ritchie, D.A. Doing Oral History: A practical guide . Second Edition. New York, (2003). ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
Williams, B.R. “Doing Video Oral History.” In Ritchie, D. (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Oral History, New York (2011), pp. 267-276. ↩︎ ↩︎
Lichtblau, A. “Case Study: Opening Up Memory Space: The Challenges of Audiovisual History.” In Ritchie, D. (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Oral History , New York (2011), pp. 277-284. ↩︎
New York Public Library. “Dance Oral History Project” Available at: https://www.nypl.org/oral-history-project-dance [Accessed 24 April 2020]. ↩︎
Baum, W.K., Oral History for the Local Historical Society, Third Edition Revised. Nashville (1978). ↩︎
Matusiak, K. K., Taylor, A., Newton, C., and Polepeddi, P. “Finding access and digital preservation solutions for a digitized oral history project: A case study” Digital Library Perspectives , 33.2 (2017): 88-99. ↩︎ ↩︎
USC Shoah Foundation. “Dimensions in Testimony” Available at: https://sfi.usc.edu/dit [Accessed 24 April 2020]. ↩︎
Hughes, J., “Taking the Leap: Including Video in Audio Oral Histories” Oral History Australia Journal , 37 (2015): 63-71. ↩︎ ↩︎
Whatley, S. “Documenting Dance: Tools, Frameworks and Digital Transformation.” In Sant, T. (ed.), Documenting Performance : The Context and Processes of Digital Curation and Archiving , London and New York (2017a), pp. 283-304. ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
Corin, F. “Steve Paxton’s Material for the Spine: The Experience of a Sensorial Edition.” In M. Bleeker (ed.), Transmission in Motion: The Technologizing of Dance , London and New York (2017), pp. 32-40. ↩︎ ↩︎
Open Ended Group. “Ghostcatching” Available at: http://openendedgroup.com/artworks/gc.html [Accessed 24 November 2019]. ↩︎ ↩︎
Whatley, S. “The Poetics of Motion Capture and Visualisation Techniques: The Differences between Watching Real and Virtual Dancing Bodies.” In Reynolds, D. and Reason, M. (eds.), Kinesthetic Empathy in Creative and Cultural Practices , London (2012), pp. 264-279. ↩︎
Kozel, S., Gibson, R., and Martelli, B. “The Weird Giggle: Attending to Affect in Virtual Reality” Transformations , 31 (2018): 1-24. ↩︎
Boyd, D., “Achieving the Promise of Oral History in a Digital Age” ,In Ritchie, D. (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Oral History , New York (2011), pp. 285-302. ↩︎
Boucher, M. , “Virtual Dance and Motion-Capture” Contemporary Aesthetics, 9. Available at: https://contempaesthetics.org/newvolume/pages/article.php?articleID=614 [Accessed 10 November 2019]. ↩︎
Jensenius, A. R. “Some Video Abstraction Techniques for Displaying Body Movement in Analysis and Performance” LEONARDO , 46.1 (2013): 53-60. ↩︎ ↩︎
McCormick, J., Hossny, M., Fielding, M., Mullins, J., Vincent, J.B., Hossny, M., Vincs, K., Mohamed, S., Nahavandi, S., Creighton, D. and Hutchison, S. “Feels Like Dancing: Motion Capture–Driven Haptic Interface as an Added Sensory Experience for Dance Viewing” LEONARDO , 53.1 (2020): 45-49. ↩︎ ↩︎
Cisneros, R.E., Wood, K., Whatley, S., Buccoli, M., Zanoni, M. and Sarti, A. “Virtual Reality and Choreographic Practice: The Potential for New Creative Methods” Body, Space and Technology , 18.1 (2019): 1-32. ↩︎
. Cobb, S. V. G., Nichols, S., Ramsey, A. and Wilson, J. R. “Virtual reality-induced symptoms and effects (VRISE)” Presence , 8.2 (1999):169–186. ↩︎
Madary, M. and Metzinger, T. K. “Real virtuality: A code of ethical conduct; Recommendations for good scientific practice and the consumers of VR-technology” Frontiers in Robotics and AI , 3.3 (2016): 1–23. ↩︎
Frank, A. W. The Wounded Storyteller: Body, Illness, and Ethics . Chicago (1995). ↩︎
Hawkins, A. H. Reconstructing Illness: Studies in Pathography , 2nd edition, West Lafayette (1999). ↩︎ ↩︎
Winslow, M. and Smith, G. “Medical Ethics and Oral History.” In Ritchie, D. (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Oral History , New York (2011), pp. 372-392. ↩︎ ↩︎
Mermikides, A. and Bouchard, G. (Eds.). Performance and the Medical Body. London (2016). ↩︎
Jamison, K. R. An Unquiet Mind. New York (1996). ↩︎
. Davies, K. “Silent and Censured Travellers”? Patients’ Narratives and Patients’ Voices: Perspectives on the History of Mental Illness since 1948” Social History of Medicine , 14.2 (2001): 267-92. ↩︎ ↩︎
. The British Library. “Oral Histories of Disability and Personal and Mental Health” Available at: https://www.bl.uk/collection-guides/oral-histories-of-personal-and-mental-health-and-disability [Accessed 01 May 2020]. ↩︎
Monash University, School of Philosophical, Historical and International Studies. “Australian Generations Oral History Project” Available at: https://www.monash.edu/arts/philosophical-historical-international-studies/australian-generations [Accessed 01 May 2020]. ↩︎
The Schizophrenia Oral History Project. Available at: https://schizophreniaoralhistories.com/ [Accessed on 01 May 2020]. ↩︎
Carel, H., Illness: The Cry of the Flesh (The art of living), New York (2013). ↩︎ ↩︎
Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance: DBSA. “DBSA SUPPORT GROUPS: An Important Step on the Road to Wellness” Available at: https://www.dbsalliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/DBSA_SUPPORT_GROUPS.pdf [Accessed 13 May 2020]. ↩︎
Halprin, A. “Portrait.” Available at: https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/65a512d0-aa03-0133-bcae-60f81dd2b63c [Accessed 22 November 2019]. ↩︎
Halprin, A. “Intensive Care, Reflections on Death and Dying.” Available at: https://digitalcollections.nypl.org/items/3bcc1450-342a-0131-a70d-685b35830967 [Accessed 22 November 2019]. ↩︎
New York Live Arts. “Still/Here | New York Live Arts” Available at: https://newyorklivearts.org/repertory/stillhere/ [Accessed 24 November 2019]. ↩︎
Kozel, S. Closer: Performance, Technologies, Phenomenology . Cambridge (2007). ↩︎ ↩︎
Smith-Nunes, G., Shaw, A., and Neale, C. “PainByte: Chronic Pain and Biomedical Engineering Through the Lens of Classical Ballet & Virtual Reality” Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction , Stockholm, Sweden (March 2018). ↩︎
Vincs, K. “Virtualizing Dance.” In Rosenberg, D. (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Screendance Studies , New York (2016), pp. 263-282. ↩︎
Hutchison S. and Vincs, K. “Dancing in Suits: A Performer’s Perspective on The Collaborative Exchange Between Self, Body, Motion Capture, Animation and Audience” in Leland, K., Fisher, L. and Harley, R. (eds.), Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium of Electronic Art , ISEA2013, Sydney (2013), pp. 1-4. ↩︎
Eddy, M. “A brief history of somatic practices and dance: historical development of the field of somatic education and its relationship to dance” Journal of Dance and Somatic Practices , 1.1(2009): 5-27. ↩︎
Sant, T. (ed) Documenting Performance : The Context and Processes of Digital Curation and Archiving . London and New York (2017). ↩︎
Hachimura, K. “Digital Archiving of Dancing” Review of the National Center for Digitization , 8 (2006): 51-66. ↩︎
Cisneros, R.E., Stamp, K., Whatley, S. and Wood, K. “WhoLoDancE: Digital tools and the dance learning environment” Research in Dance Education , 20 . 1 (2019): 54-72. ↩︎
Skinner, C., Tyas, P., and Street, A. Artists in the archives toolkit: A toolkit for best practice . Wiltshire (2015). Available at: https://theartsinwiltshire.files.wordpress.com/2015/04/artist-archive-doc-final.pdf. [Accessed 1 October 2019]. ↩︎
Post, C. “Preservation Practices of New Media Artists: Challenges, Strategies, and Attitudes in the Personal Management of Artworks” Journal of Documentation , 73.4 (2017): 716-732. ↩︎
MacDevitt, J. “The User-Archivist and Collective (In)Voluntary Memory: Read/Writing the Networked Digital Archive.” In Gardiner, H. and Bailey, C. (eds.), Revisualising Visual Culture , London (2012), pp. 109-124. ↩︎
Candy, L. “Practice Based Research: A Guide. CCS Report: 2006-V1.0 November.” Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257944497 [Accessed 27 February 2020]. ↩︎
Nelson, R. Practice as Research in the Arts: Principles, Protocols, Pedagogies, Resistances . Houndsmill, Pelgrave (2013). ↩︎